This year marks the 75th anniversary of the United Nations, the time the world is fighting against COVID-19 that has greatly challenged the world through devouring the lives and destroying the global economy.
In the spirit of South-South cooperation (SSC), developing countries are helping each other respond to the pandemic, including sharing experience on how to curb the virus spreading and launch lots of funds and projects to support improvement of health-care quality and vaccine research.
Actually, the SSC since the new century has been greatly upgraded, moving from traditional trade and economic aid to market-based trade, finance, investment, industrial cooperation, and regional integration.
South-South cooperation is the cooperation among developing countries, mostly located in the south of the planet, based on the common historical experience and the common tasks after independence.
The UN history of SSC dates back to 1949 with the establishment of the first UN technical aid program by the Economic and Social Council.
In 1955, the first Asian-African Conference (also known as Bandung Conference) held by Asian and African states, most of which were newly independent, proposed implementing financial and technical cooperation among developing countries.
The adoption of series of conventions, such as the "United Nations Convention on International Multimodal Transport of Goods" in 1980, promoted by the Group of 77, one of the two largest international organizations for SSC in the early 1960s besides the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM), has played an active role in the substantial growth of transnational cargo and personnel transportation in the 1980s and further development of global economic exchanges.
In 1965, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) was founded by the UN, becoming the permanent agency of the United Nations in developing countries together with the Economic and Social Council founded in 1945.
To further advocate for and coordinate South-South and triangular cooperation globally, the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC) hosted by UNDP was established by the UN General Assembly in 1974.
The Buenos Aires Plan of Action (BAPA) for Promoting and Implementing Technical Cooperation among Developing Countries (TCDC) adopted by 138 UN Member States in 1978 is regarded as one of the main pillars for SSC, which has defined a series of recommendations in order to establish legal frameworks and financing mechanisms at the national, regional, interregional and global levels.
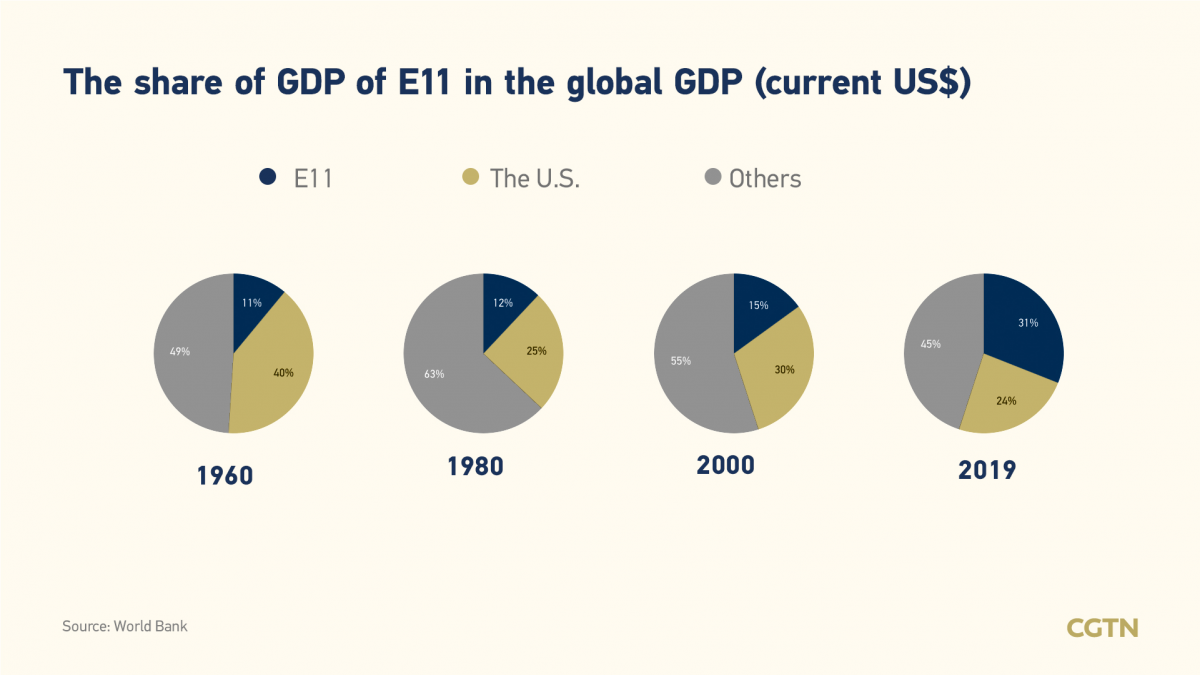
Since the 21st century, emerging economies like China have developed rapidly, playing a more and more vital role in the world economy. According to data from the World Bank, calculated at the current U.S. dollar exchange rate, the share of the major emerging economies, defined as "E11", (including the economies of Argentina, Brazil, China, India, Indonesia, the Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa and Turkey) in global GDP has increased from 11 percent in 1960 to 31 percent in 2019, clearly exceeding the share of the United States.
Also, huge differences are seen among most developing countries embracing market economy, as now there are both newly industrialized countries, countries with low economic development levels, as well as energy-exporting countries that are wealthy but with a single economic structure, which requires them to adopt different industrial policies and provides a foundation for various economic cooperation.
The form of SSC before mainly includes the establishment of economic cooperation union between governments, reciprocity in trade, and economic assistance.
In addition, most of the cooperation is led by the government, lacking in broad participation of enterprises, especially private enterprises. Thus, SSC is greatly influenced by politics and even more belongs to political cooperation with limited economic effects.
In recent twenty years, the SSC has been greatly expanded to more fields except for traditional trade and economic aid.
Besides traditional inter-industry trade between such as resources and manufactured goods among countries, there is also intra-industry trade based on the division of labor in the industrial chain as well as intra-product trade based on the division of labor within multinational companies.
Also, international direct investment among developing countries has developed rapidly, promoting industrial transfer, the industrial division of labor, and industrialization.
Regional integration has been an important part of economic cooperation among developing countries in recent years, with bilateral and multilateral free trade agreements, free trade zones, and regional integration organizations emerging one after another.
And there are more financial cooperation models, including regional financial institutions, development banks, investment funds, inter-regional currency swaps, and local currency settlements.
"The facts speak for themselves", United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres said. According to UNOSSC, in recent years, the countries of the South have contributed to more than half of the world's growth. Meanwhile, intra-south trade is higher than ever, accounting for more than a quarter of all world trade, and the outflows of foreign direct investment from the South represent a third of the global flows.
WTO data shows that all countries except Somalia have signed regional trade agreements (RTAs) with other countries. From September 2007 to early January 2011, 43 new RTAs implemented worldwide, with one-third of which launched among emerging economies in Asia.
There are also cooperative groups established to safeguard the common interests of developing countries in international economics, such as the BRICS Group, the E11, as well as the New Development Bank.
As Chinese Vice Premier Hu Chunhua said during the opening session of the Second High-level UN Conference on SSC in Argentina last year, China is a firm supporter, active participant and an important contributor to the SSC.
As a new SSC model, the triangular cooperation involves three actors, two from the South and one from the North or an international organization that provides the financial resources so that the countries of the South can exchange technical assistance on a specific topic.
In what is considered as a flagship project of triangular cooperation beginning in 2014, China has participated two projects on renewable energy technology transfer with Ghana and Zambia funded by Denmark by providing experience and technical skills to help rural communities in Ghana and Zambia gain access to electricity.
Meanwhile, the Belt and Road Initiative leaves a lot of flexibility for participators to decide how to engage in the initiative, Jorge Chediek, Director of UNOSSC, once said.
"Many cities in the countries along the Belt and Road have joined the Initiative, which will promote SSC and sustainable development," said Chediek during the 2020 China International Fair for Trade in Services in Beijing just closed Wednesday, noting that China has made important contributions to SSC and the rise of developing countries.
"Also, China has provided an example on how to fight the pandemic...and many of its experience is worthy of global reference," he addressed.
Reported ob September 12 2020 by CGTN (China).